Path to Gaucher Diagnosis
Our service is ideal for identification of Gaucher Disease in at-risk patients showing specific clinical symptoms or for an individual or family member who has a family history of Gaucher Disease.
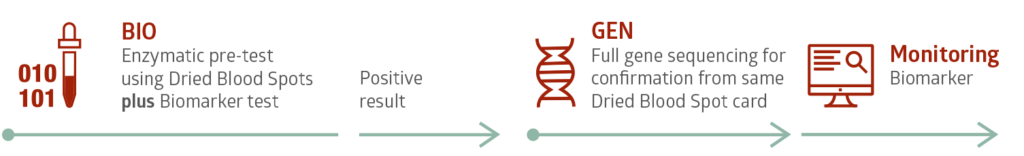
Testing is fast and safe using Dried Blood Spot (DBS) cards. This simple and minimally invasive technique supplies enough sample for biochemical testing and in most cases genetic confirmation testing as well.
Available enzyme, biomarker, and genetic tests:
| Disease | Enzyme Tests | Biomarker Tests | Genetic Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gaucher Disease | GBA (acid β-glucosidase) | Lyso-GL-1 (Lyso-Gb1) | GBA |
Differential diagnosis options:
| Disease | Enzyme Tests | Biomarker Tests | Genetic Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASMD (Niemann-Pick Type A/B) | ASM (acid Sphingomyelinase) | Lyso-SPM (Lyso-Sphingomyelin) | SMPD1 |
| Niemann-Pick Type C1/D | -- | -- | NPC1 |
| Niemann-Pick Type C2 | -- | -- | NPC2 |
| Lysosomal acid Lipase Deficiency (LALD) | LAL (lysosomal acid Lipase) | -- | LIPA |
Quality:
Fully validated and accredited* according to the highest quality standards for Medical Laboratories (ISO 15189).
Methodologies:
- Enzyme and biomarker assays by Clinical Mass Spectrometry.
- Genetics by Sanger and Next-Generation Sequencing platforms.
About Gaucher Disease
What is Gaucher Disease?
Gaucher disease is part of a group of lipid storage disorders affecting lipid metabolism in lysosomes. It is caused by a genetic mutation and results in a toxic accumulation of the metabolic substrate glucocerebroside.
Gaucher disease has 3 different types:
- GD type I (non-neuropathic) is the most common and least severe form of the disease. Symptoms may begin early in life or in adulthood. The range and severity of symptoms can vary dramatically between patients.
- GD type II (acute infantile neuropathic) typically begins within 6 months of birth, and affected children usually die by age two.
- GD type III (chronic neuropathic) can begin at any time in childhood or even in adulthood and is characterized by slowly progressive, but milder neurologic symptoms compared to the type II version. Patients often live in early adolescence and adulthood.
Which mutation causes an enzyme deficiency?
Gaucher (GD) is caused by a mutation in the GBA gene which encodes the enzyme glucocerebrosidase. When this enzyme is deficient or improperly functioning, glucocerebroside accumulates in the body, primarily in white blood cells and especially macrophages. Glucocerebroside also builds up in the spleen, liver, kidneys, lungs, brain, and bone marrow.
Are there diseases similar symptoms to Gaucher Disease?
Clinical presentation of Gaucher Disease is similar to other congentital sphingolipidoses which can result in underdiagnosis.
How to Order Gaucher Diagnostic Services

Our Diagnostic Service for Gaucher disease includes enzyme testing for acid β-glucosidase (GBA), biomarker testing for Glucosylsphingosine (Lyso-GL-1 / Lyso-Gb1) as well as any necessary genetic molecular analysis.
All of our services are available to any interested physician or healthcare professional worldwide.
As part of our diagnostic services, we supply complimentary ARCHIMEDlife sampling kits. You can order your sampling kits and diagnostic services through our easy and secure WEBPORTAL and receive your electronic medical report in five simple steps.
Five Simple Steps
1Order Sampling Kit
2Collect the Sample
3Register the DBS Card
4Return the Sample
5Receive your Report