Path to Fabry Diagnostics
Our service is ideal for the identification of Fabry disease in at-risk patients showing specific clinical symptoms or for an individual or family member who has a family history of Fabry disease.
Testing is fast and safe using Dried Blood Spot (DBS) cards. This simple and minimally invasive technique supplies enough sample for biochemical testing and in most cases genetic confirmation testing as well.
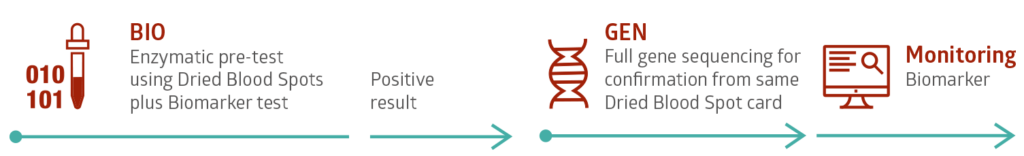
Available enzymatic, biomarker, and genetics tests:
| Disease | Enzyme Tests | Biomarker Tests | Genetic Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fabry Disease | GLA (α-Galactosidase A) | Lyso-GL-3 (Lysp-Gb3) | GLA |
Quality:
Fully validated and accredited* according to the highest quality standards for Medical Laboratories (ISO 15189).
Methodologies:
- Enzyme and biomarker assays by Clinical Mass Spectrometry.
- Genetics by Sanger and Next-Generation Sequencing platforms.
About Fabry Disease
What is Fabry disease?
Fabry disease (FD) is a rare X-linked inherited disorder where deficiency of the α-Galactosidase A (α-Gal A) enzyme causes Globotriaosylceramide (GL-3/Gb3) lipid accumulation in the cells of different organs. The multiple organ involvement in Fabry disease causes damage which progresses over several decades. It can result in end-stage kidney disease, cardiovascular disease, and reduced life expectancy.
There are two phenotypes of Fabry disease:
- Classical form (early-onset) – Patients with this form have very little or no enzyme activity and clinical symptoms appear in early childhood or adolescence.
- Non-classical form (late-onset) – Patients with this form have some enzyme activity and normal development. Symptoms begin to appear from early adulthood.
Which mutation causes an enzyme deficiency?
Fabry disease is caused by different mutation variants in the GLA gene, the gene responsible for coding the α-Gal A enzyme which metabolizes GL-3/Gb3. A reduction in α-Gal A activity below a certain level and an increase in the concentration of the sphingolipid Lyso-GL-3 (Lyso-Gb3) will support a diagnosis of FD.
Can women be affected by Fabry disease?
Because Fabry disease is an X-linked inherited disorder, the disease primarily affects men, however, due to random X-chromosome inactivation, women can potentially be affected with either form of the disease. Enzyme testing is less effective in these women and evidence shows that biomarker testing in combination with enzyme testing substantially improves the detection of Fabry disease in females[1,2,3].
Are Fabry disease symptoms similar to other diseases?
The symptoms of FD are often non-specific and resemble those of other conditions. They can appear at different stages of the disease or some symptoms not at all, depending on which organs are being affected. Consequently, FD is often misdiagnosed or delayed in diagnosis.
How to Order Fabry Disease Diagnostic Services

Our Diagnostic Service for Fabry Disease includes enzyme testing for α-Galactosidase A, biomarker testing for Lyso-GL-3 (Lyso-Gb3) as well as any necessary genetic molecular analysis.
All of our services are available to any interested physician or healthcare professional worldwide.
As part of our diagnostic services, we supply complimentary ARCHIMEDlife sampling kits. You can order your sampling kits and diagnostic services through our easy and secure WEBPORTAL and receive your electronic medical report in five simple steps.
Five Simple Steps
1Order Sampling Kit
2Collect the Sample
3Register the DBS Card
4Return the Sample
5Receive your Report
References
- Diagnostic strategy for Females suspected of Fabry Disease, Poster Presentation, WORLDSymposium, Feb. 2020, Orlando USA
- Balendran S, Oliva P, Sansen S, et al., Diagnostic strategy for females suspected of Fabry disease. Clin Genet. 2020;97(4):655-660.
- Stiles AR, Zhang H, Dai J, et al. A comprehensive testing algorithm for the diagnosis of Fabry disease in males and females. Mol Genet Metab. 2020;130(3):209-214.