Path to Pompe Disease Diagnosis
Our service is ideal for the identification of Pompe Disease in at-risk patients showing specific clinical symptoms or for an individual or family member who has a family history of Pompe Disease.
Testing is fast and safe using Dried Blood Spot (DBS) cards. This simple and minimally invasive technique supplies enough sample for biochemical testing and in most cases genetic confirmation testing as well.
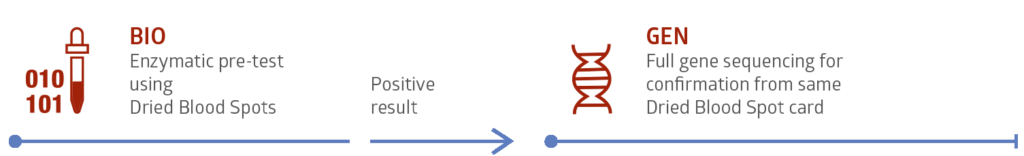
Available enzymatic and genetics tests:
| Disease | Enzyme Tests | Biomarker Tests | Genetic Tests |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pompe Disease | GAA (acid α-Glucosidase) | -- | GAA |
Differential diagnosis options:
Other disease affecting muscle function and growth such as 5q-Spinal Muscular Atrpohy (SMA) and Limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) are a differential diagnosis of Pompe disease. Visit our Muscle Disorders page for more information.
Quality:
Fully validated and accredited* according to the highest quality standards for Medical Laboratories (ISO 15189).
Methodologies:
- Enzyme assays by Clinical Mass Spectrometry.
- Genetics by Sanger and Next-Generation Sequencing platforms.
About Pompe Disease
Pompe Disease, also known as glycogen storage disease type II or acid maltase deficiency (AMD), is part of a group of lipid storage disorders affecting glycogen metabolism in lysosomes. Pompe disease is an inherited autosomal recessive genetic disease resulting from the reduced or absent activity of the enzyme acid α-Glucosidase (GAA).
There are two main forms of Pompe disease
- Classic infantile – Characterized by a total lack of GAA activity and by a rapid buildup of glycogen in skeletal muscle and heart. This form is the most severe and while symptoms may not be apparent at birth, the disease usually presents within the first three months of life with rapid, progressive muscle weakness (floppy infants), diminished muscle tone (hypotonia), respiratory insufficiency, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. These problems together culminate in cardio-respiratory failure within the first 2 years of life.
- Childhood/adult (late onset) – Childhood and adult Pompe disease is associated with progressive weakness of mainly the proximal muscles (limb-girdle, upper arms, and upper legs), and varying degrees of respiratory weakness due to dysfunction of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles. As a result of the combination of these serious symptoms, affected individuals may become wheelchair and/or ventilator dependent.
Which mutation causes an enzyme deficiency?
Pompe Disease is caused by different mutations in the GAA gene. This gene is responsible for coding the GAA enzyme which metabolizes glycogen. Accumulation of the glycogen, occurring primarily in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle results in the clinical presentation of the disease.
Are there diseases similar symptoms to Pompe Disease?
Because of the progressive muscle weakness associated with Pompe disease, it shares symptoms of other muscular disorders such as Spinal Muscular Atrophy or Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy. Investigation of these disorders should be considered with individuals showing non-specific symptoms.
How to Order Pompe Disease Diagnostic Services

Our Diagnostic Service for Pompe Disease includes a rapid enzyme test for acid α-Glucosidase as well as any necessary genetic molecular analysis.
All of our services are available to any interested physician or healthcare professional worldwide.
As part of our diagnostic services, we supply complimentary ARCHIMEDlife sampling kits. You can order your sampling kits and diagnostic services through our easy and secure WEBPORTAL and receive your electronic medical report in five simple steps.
Five Simple Steps
1Order Sampling Kit
2Collect the Sample
3Register the DBS Card
4Return the Sample
5Receive your Report